During my years as web developer and designer (which, I am not entirely sure if this is still valid), I have been to only two Google’s conferences; Google Developer Group (GDGKL) and Google Webmaster Conference (WMCKL) which the later focus on search engine optimisation or Google SEO. And the later happened on previous Friday, August 2nd, 2019.
Hello Google Search Console
It was about their tool called Google Webmaster, which has been rebranded as Google Search Console. Mainly, it was about Google SEO tools and best practices, and not to forget busting some myths that linger around the topic. I will try to share and compile the things that were discussed at the event.
They even held a special session to discuss about how Google Search look at links. Very informational.
The Basics of Google SEO
They presented about how does the search engine works. How to get listed (indexed) by Google Search is to start get linked by other sites, social network included. Then, you should submit your sitemap to Google Search Console, to inform the engine to start crawling your site. Done.
Info: Google Analytics does not share its data to Google Search.
Along the way, there will be Core Algorithm Updates which was done to ensure they can and will return the most relevant result to their users. Do not fear this changes, fear that you will not change for your target user instead.
Quick Tip:
Create content from a user perspective. Serve and solve their issues, in the most comfortable and easy way to understand for the end user. Stop trying to ‘gamify’ the Core Algorithm.
Abdus Fauzi
10 Google SEO Tips
The first two is very important because these are the informations that will be shown in the search result. Keep in mind, Google Search algorithm is getting smarter by the day (or year). It has the ability to decide what best to show in the result page. They told us that there are about 200 signals that will be collected and computed to rank and return the result for every search request.
These are some of the highlight keypoints, but not limited to them.
1. Title
Make sure you optimise your title for Google Search result. There is limited space available. Avoid complex and confusing title. This will be extracted from <title> tag.
2. Description
Write a concise description or what you may know as excerpt. There are many plugins/tools that can help with generating this, but do ensure that it was written as short and brief, but comprehensive as possible. Extracted from <meta name="description" content="...">.
However, the search engine is quite intelligent. It can generate its own description from your page and content, to meet search result’s relevency. It is good to know that you can help Google to describe the page.
3. URL or permalink
This is one of the element that will be shown in the search result. Despite all that, there are time when Google Search will replace this with another information, such as breadcrumb.
4. Structured Data
In addition, you can implement this many ways, either in JSON-LD format, or follows Schema.org Markup. For WordPress users, Yoast SEO v11 already implemented this for you in JSON-LD. You can find this in your <header> element. We will also talk more about this later.
5. Links
Link internally and externally using anchor tag <a href="...">. However, we will talk about this in detail, later.
6. Image ALT
This is an image related technique, that also helps with Google SEO. Do describe the image using the <img alt=""> attributes because it informs Google with more description of the image. They can use their Machine Learning tool to help, but this attribute helps them more. Win win. Filename renaming technique is not wrong, but it will give very little impact. More discussion on Google Image Search later.
7. Speed
This has something to do with User Experience. Focus on First Contentful Paint (FCP). You may ignore the ‘total page load time’. Some websites will load more content through ajax. This will give false-negative to your page load time.
8. Robots.txt
Use this yet to be standardised feature to craft how crawlers can index your site. Read more about robots.txt. You can block certain portion of your site from ethical search engine bots. Like, do not block access to your images directory, unless you have a solid reason to do so. Read point 6.
9. Canonical Tag
This one is related to how you structure your content. A proper canonical <meta> tag can helps with Google Search understanding your content structure. You might have duplicate or near-duplicate content, and would like to focus them on specific master content. Implement canonical tag.
10. hreflang Tag.
A powerful, and yet can be complicated. Very useful for sites with multiple languages. This will helps Google Search to deliver the right contant in the right language for the right user. If they’re coming from Malaysia, probably in Malay. If the request comes from Paris, deliver them the French version. Google will ensure the best match for any search request. Ahrefs explain this nicely.
Structured Data for Google SEO
Additional information to further expand definitions of the content for search engine (Google SEO).
Google Search crawling bots will look into this data, and use it to suppliments more information for indexing and categorising the content. With structured data, we can inform the type of the content to the Core Algorithm, as per listed on the Structured Data Reference page.
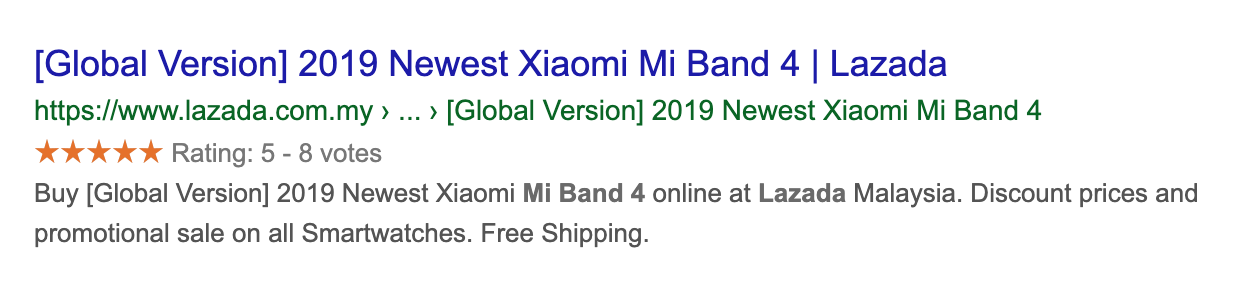
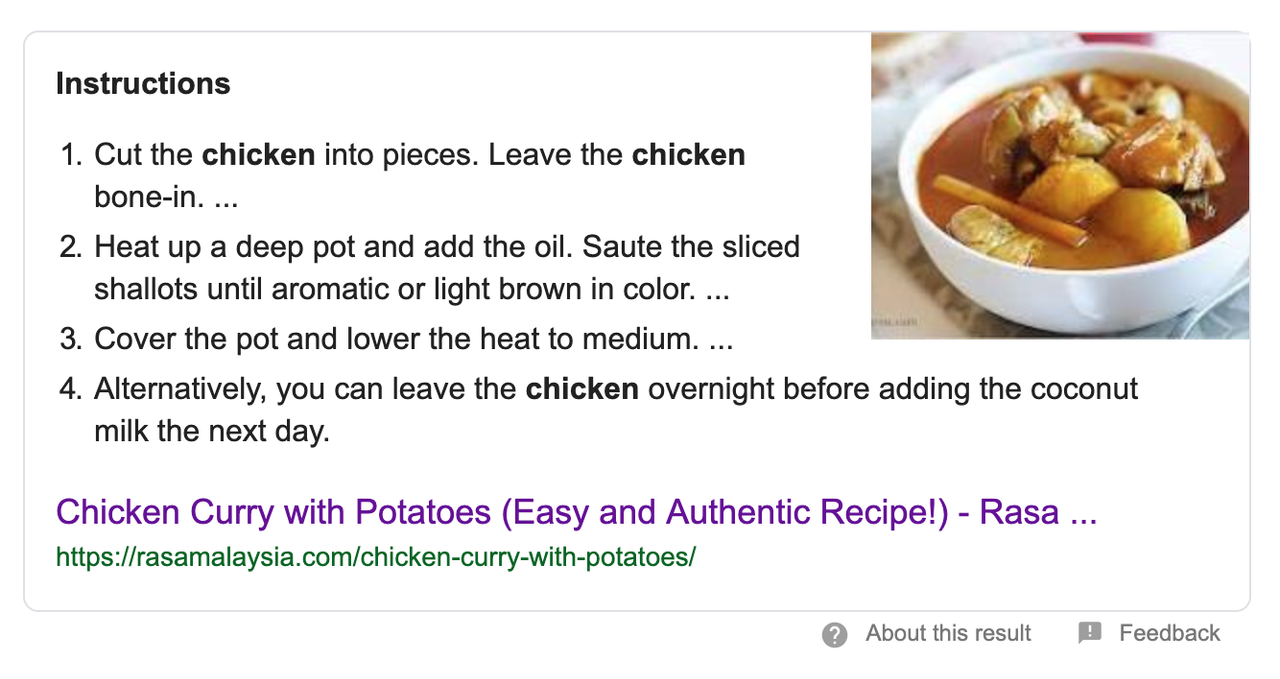
Therefore, you can define your content type as article, event, FAQ, Q&A, how-to, product, etc. Below are the samples use case of structured data which reflected on search results:
Search for product with Google SEO
Search for places/service
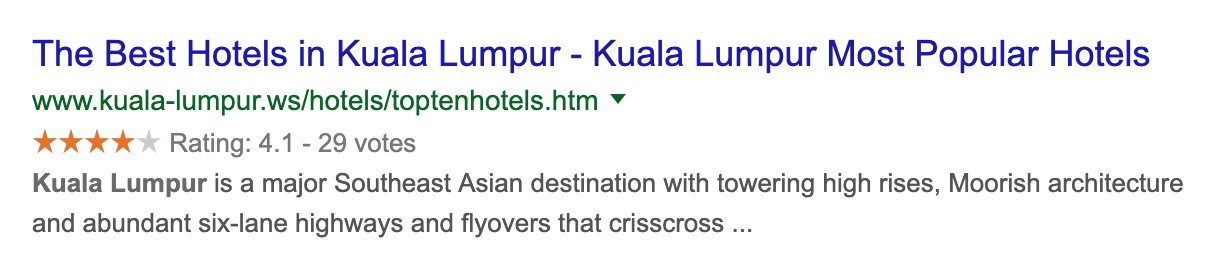
Result in card format (with visuals)

Search for how-to or recipe




[…] Google SEO: Face to Face […]